I have designed a new set of RMCE landing sites and integration plasmids that permit creation of new transgenic animals in as little as eight days (Nonet, 2023). The method is much more efficient than the prior method and can be multiplexed.

Traditional RMCE
Rapid RMCE
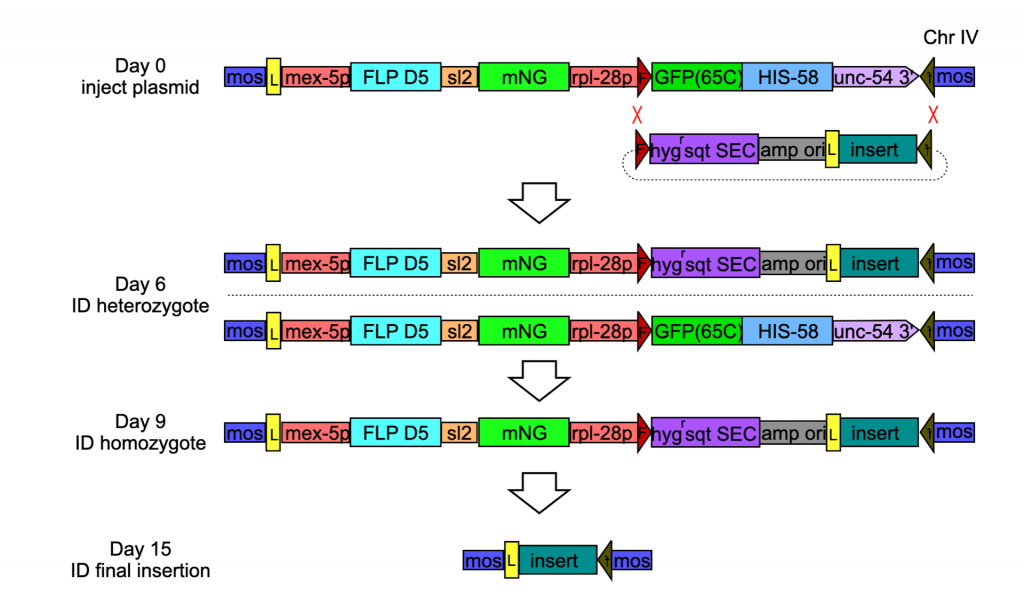
The published RMCE approaches require the use of a Self Excising Cassette (SEC) which contains the screening/selection marker and a heat shock Cre transcription unit to permit removal of the SEC. This process takes an addition 2 to 3 generations before a new transgene can be utilized. One generation to amplify the homozygotes for heat shock, then one to two generations to isolate a homozygous animal with the cassette excised. In addition, if one is using a two-component RMCE approach an additional two generations are required to cross out the source of FLP.
The new approach creates a myo-2p::mNG (or GFP, Scarlet or BFP) marked RMCE insertion by selection for hygromycin resistance. The ‘final’ transgene contains the myo-2p::FP and hygR gene cassettes, the pBluescript backbone as a spacer, and then an insert of choice. The myo-2p::FP, hygR and pBluescript backbone portion of the insertion is flanked by loxP sites which permits excision of this region at very high efficiency to create an unmarked transgene by crossing through a mex-5p Cre line.
To create such a transgene, one clones a sequence of interest into pHygG2 (or a similar vector – rRMCE vectors) using either traditional cloning or SapI-based Golden Gate cloning approaches. One then injects the DNA into an appropriate landing site strain (on Chr I, II, or IV – rRMCE landing sites) and adds hygromycin to the injection plates at day 3. On day 8 one isolates L4 homozygous insertions. The homozygous animals are easily identified as animals that survive on hygromycin and express only mNG (in the case of pHygG2) in pharyngeal nuclei. The approach is efficient yielding an insertion in ~50% of injected animals.
In addition, I used a two-step approach to create landing sites for this drug selection method which greatly simplifies creating additional custom landing sites that use a distinct promoter from myo-2p to mark the inserts (customizing landing sites).
References
Nonet, M. (2023). Rapid generation of C. elegans single copy transgenes combining RMCE and drug selection. Genetics iyad072. PMID:37079426 [Abstract] [PDF]
We strive to provide accurate information about the plasmids and methods we have developed. Please let us know if you find an error, find missing or errant links, find statements in this webpage erroneous or confusing , or have other suggestions that could improve this website.
last updated 8-3-2023