The functional consequences of fat accumulation in muscle
The accumulation of adipocytes within skeletal muscle is a nearly ubiquitous feature of muscle pathology – associated with conditions as diverse as aging, diabetes and tendon injury. Though this fat accumulation is frequently associated with poor muscle strength in humans, a direct link has not been established due to systemic disease pressures that simultaneously affect muscle cells. Recently, we have developed methodology for high-resolution mapping of intramuscular adipocytes in mouse muscle that we are using in conjunction with precision ex-vivo analysis of muscle contractile performance to define the direct effect of fat accumulation on muscle function. Ongoing work in this area is investigating the effect of fat accumulation on hypertrophic signaling and the potential for dynamic forces (resistance exercise) to reverse this pathology. Check this and this out.
The role of fat phenotype in fat-muscle cross-talk

The way we think about the function of fat in the body has changed dramatically over the past 10 years. Fat is now recognized as one of the most important endocrine regulators of body physiology – affecting a diversity of cells from neurons to osteoblasts. However, despite the close proximity of muscle and fat (specifically inter-muscular adipose tissue – IMAT), we know very little about how these tissues might signal each other locally. To explore this important question, we have developed an inter-muscular fat transplant model in the mouse where we can alter fat phenotype and genotype to study the factors that influence fat-muscle cross-talk. Ongoing work on this project is exploring the role of brown and browned-beige fat signaling on muscle degeneration and regeneration. It is our hope that defining these interactions will lead to fat-targeted therapies where excessive accumulation of beige fat is impeding muscle functional recovery. Check this and this out.
The cellular basis for poor muscle performance in diabetic peripheral neuropathy

The accumulation of intramuscular fat is dramatic in diabetic peripheral neuropathy – replacing as much as 90% of the volume of muscles of the foot and calf. To better understand the interaction between these intramuscular adipocytes and neighboring muscle fibers in humans, we are obtaining biopsies from participants undergoing amputation, separating the muscle and fat components and isolating progenitor cells. Using these cells we can generate patient-specific co-culture models to study paracrine secreted factors from intramuscular fat and how those signals regulate myogenesis. Check this out.
Guiding cell-based therapies to prevent fibrosis

Fibrosis is a prevalent and debilitating feature of soft tissue injury. Current treatment strategies are unable to fully prevent tissue fibrosis and frequently individuals are left with decreased range of motion and functional deficits. Currently, we are exploring alternative sources of human adipose progenitor cells (APCs) and culture conditions to assess depot-specific mechano-sensing and fibrotic conversion during expansion. Check this and this out.
Post-translational control of EC-Coupling
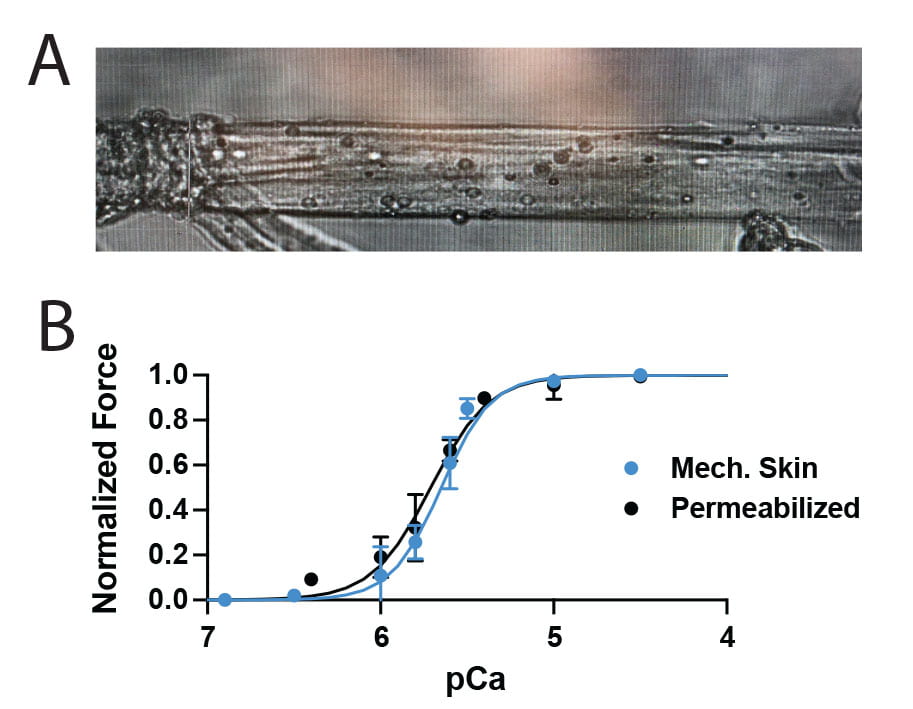
We are embarking on a new project to understand how EC-coupling is regulated by post-translational modifications. We have evidence that acetyltransferases p300/CBP are critical for muscle contraction, but the mechanism has yet to be determined. Check this out. Our preliminary data support post-translational acetylation of protein(s) involved in EC coupling. We are using mechanically skinned isolated myofibers and engineered muscle microtissues where each component of EC-coupling can be tested in isolation to prove this and further hone the mechanism. You could be the one to figure it out! Apply to post-doc with us today!