I use computational structural biology to help biomedical researchers approach their question from a molecular viewpoint. I can contribute a mechanistic hypothesis, structural analysis, or the interpretation of experimental results in the context of a protein’s structure-function relationship. If you have a question like “How does this mutation cause that condition?” then we should talk.
Contact
Jonathan Sheehan PhD
10621 BJC Institute of Health Bldg.
(314) 273-8368
jonathan.sheehan@wustl.edu

Research Interests

Disease mechanism discovered using in-silico mutational analysis
By mapping intracellular mutations onto an atomic model of Kir1.1, we found that several are localized to an immunoglobulin (Ig)-like domain (IgLD). Thermodynamic calculations on computationally mutated channels suggest that the IgLD core residues are among the most important residues for determining cytoplasmic domain stability. Consistent with this notion, we show that two Antenatal Barter Syndrome mutations located within the IgLD core impair channel biosynthesis and trafficking in mammalian cells. Our study sheds new light on the pathogenesis of ABD and establishes the IgLD as an essential structure within the Kir channel family.

Energetic analysis of deletion mutant provides rationale for drug choice
A patient with an ER+ breast cancer showed a novel deletion in the C2 domain of the PIK3CA gene. The structure of p110α (green) bound to p85α (red) is known. Computational modeling of the deletion mutant allowed comparison between PIK3CAWT p110α (cyan) and the deletion (orange). Specific favorable inter-residue contacts were identified that would be lost as a result of the deletion, predicting a significant decrease in binding energy. Coimmunoprecipitation experiments showed reduced binding of the C2 deletion mutants with p85 compared with wild-type p110α. The MCF10A cells expressing PIK3CA C2 deletions exhibited growth factor-independent growth, an invasive phenotype, and higher phosphorylation of AKT, ERK, and S6 compared with parental MCF10A cells. All these changes were ablated by alpelisib treatment. Conclusions: C2 domain deletions in PIK3CA generate PI3K dependence and should be considered biomarkers of sensitivity to PI3K inhibitors.

How does a frameshift mutation link FGFBP2 with sporadic IgG4-related disease?
Three family members with features of IgG4‐related disease shared a previously unreported heterozygous single base deletion in fibroblast growth factor binding protein type 2. The FGFBP2 protein is secreted by cytotoxic T‐lymphocytes and binds fibroblast growth factor. The proband and the two sons had 5- to 10-fold higher numbers of circulating cytotoxic CD4+ T cells and plasmablasts compared to matched controls. The mutation causes a frameshift in the coding sequence of the protein. In-silico protein folding of the C-terminal domain of the WT confidently predicted two alpha helices held at a fixed angle by a conserved disulfide bond. The variant sequence of the C-terminal domain is predicted to form a disordered random coil unable to adopt a stable conformation, providing a mechanistic hypothesis for this observation of involvement of FGFBP2 variants in IgG4-RD.
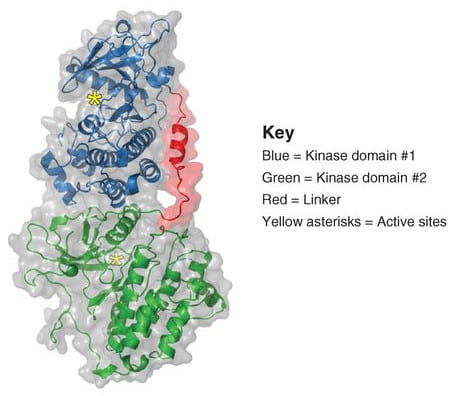
EGFR kinase domain duplication is conformationally capable of auto-activation
In analyzing the tumor from a patient, we identified a novel EGFR alteration in lung cancer: EGFR exon 18–25 kinase domain duplication (EGFR-KDD). Through analysis of a larger cohort of tumor samples, we found additional cases of EGFR-KDD in lung, brain, and other cancers. Given the presence of two tandem in-frame kinase domains within the EGFR-KDD structure, we hypothesized that EGFR-KDD could auto-activate by forming an intramolecular dimer. We modeled the EGFR-KDD structure based on the active asymmetric EGFR dimer. Conformational sampling with Rosetta demonstrated that the linker between the tandem tyrosine kinase domains allows for the proper positioning of the two domains necessary for asymmetric dimerization and intramolecular EGFR activation. EGFR-KDD was found to be constitutively active in vitro.
Teaching
Techniques in Computational Structural Biology:
Competence using Unix and command line software
- Introduction to computing in the Linux environment
- Data analysis using awk, grep, find, xargs, bash, gnuplot
- High-performance computing using batch submission on WUSM’s CHPC 2.0 cluster
Molecular Visualization and Analysis
- UCSF Chimera
- PyMol
- VMD
- RasMol
- Understanding PDB file contents, format, limitations, and alternatives
- Morphing, movie making
- Measurement of distances, angles, ligand binding analysis, mixed rendering for figures
- Electrostatic surface calculation & representation using ABPS
- Structure and domain superposition, RMSD
- Protein classification techniques: SCOP, DALI, CATH, PFAM
Sequence-based techniques
- Visual sequece alignment using Dotlet
- Needleman-Wunsch (global) vs. Smith-Waterman (local) alignment and dynamic programming
- Multiple sequence alignments using CLUSTAL
- Sequence searching using BLAST vs. PSIBlast
- Secondary structure prediction using PSIPRED
- Prediction of domains, disorder, transmembrane regions
- Machine-learning fundamentals: artifical neural networks, hidden markov models
Protein Modeling
- Simple protein modeling using fold recognition servers
- Basic comparative modeling using SCWRL
- Loop building and comparative modeling using Modeller
- Multi-template comparative modeling using RosettaCM
- Energy minimization using AMBER
- Ab-initio (De-Novo) protein structure prediction using Rosetta
- Structural clustering techniques for analyzing prediction results
Protein Docking
- Protein-protein docking using HADDOCK
- Protein-protein docking using Rosetta
Ligand Docking
- Protein-ligand docking using Autodock-Vina
- Protein-ligand docking using Rosetta
Protein Design
- Single- and multi- state protein design using Rosetta
- Computational antibody affinity maturation
- In-silico alanine scanning
- In-silico saturation mutagenesis
Ligand-based virtual screening
- Using QSAR models and virtual screening to enrich HTS follow up

Publications
IgG4-related disease: Association with a rare gene variant expressed in cytotoxic T cells.
Newman JH, Shaver A, Sheehan JH, Mallal S, Stone JH, Pillai S, Bastarache L, Riebau D, Allard-Chamard H, Stone WM, Perugino C, Pilkinton M, Smith SA, McDonnell WJ, Capra JA, Meiler J, Cogan J, Xing K, Mahajan VS, Mattoo H, Hamid R, Phillips JA 3rd; Undiagnosed Disease Network.
Mol Genet Genomic Med. 2019 Jun;7(6):e686. doi: 10.1002/mgg3.686. Epub 2019 Apr 16.
Inhibitors of the HIV-1 capsid, a target of opportunity.
Carnes SK, Sheehan JH, Aiken C.
Curr Opin HIV AIDS. 2018 Jul;13(4):359-365. doi: 10.1097/COH.0000000000000472. Review.
Sivley RM, Sheehan JH, Kropski JA, Cogan J, Blackwell TS, Phillips JA, Bush WS, Meiler J, Capra JA.
BMC Bioinformatics. 2018 Jan 23;19(1):18. doi: 10.1186/s12859-018-2010-z.
Croessmann S, Sheehan JH, Lee KM, Sliwoski G, He J, Nagy R, Riddle D, Mayer IA, Balko JM, Lanman R, Miller VA, Cantley LC, Meiler J, Arteaga CL.
Clin Cancer Res. 2018 Mar 15;24(6):1426-1435. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-17-2141. Epub 2017 Dec 28. Erratum in: Clin Cancer Res. 2019 Feb 15;25(4):1432.
Kharade SV, Sheehan JH, Figueroa EE, Meiler J, Denton JS.
Mol Pharmacol. 2017 Sep;92(3):338-346. doi: 10.1124/mol.117.108472. Epub 2017 Jun 15.
Hanker AB, Brewer MR, Sheehan JH, Koch JP, Sliwoski GR, Nagy R, Lanman R, Berger MF, Hyman DM, Solit DB, He J, Miller V, Cutler RE Jr, Lalani AS, Cross D, Lovly CM, Meiler J, Arteaga CL.
Cancer Discov. 2017 Jun;7(6):575-585. doi: 10.1158/2159-8290.CD-16-1431. Epub 2017 Mar 8. Erratum in: Cancer Discov. 2019 Feb;9(2):303.
Protocols for Molecular Modeling with Rosetta3 and RosettaScripts.
Bender BJ, Cisneros A 3rd, Duran AM, Finn JA, Fu D, Lokits AD, Mueller BK, Sangha AK, Sauer MF, Sevy AM, Sliwoski G, Sheehan JH, DiMaio F, Meiler J, Moretti R.
Biochemistry. 2016 Aug 30;55(34):4748-63. doi: 10.1021/acs.biochem.6b00444. Epub 2016 Aug 16. Review.
EGFR Fusions as Novel Therapeutic Targets in Lung Cancer.
Konduri K, Gallant JN, Chae YK, Giles FJ, Gitlitz BJ, Gowen K, Ichihara E, Owonikoko TK, Peddareddigari V, Ramalingam SS, Reddy SK, Eaby-Sandy B, Vavalà T, Whiteley A, Chen H, Yan Y, Sheehan JH, Meiler J, Morosini D, Ross JS, Stephens PJ, Miller VA, Ali SM, Lovly CM.
Cancer Discov. 2016 Jun;6(6):601-11. doi: 10.1158/2159-8290.CD-16-0075. Epub 2016 Apr 21.
The role of Bruton’s tyrosine kinase in autoimmunity and implications for therapy.
Crofford LJ, Nyhoff LE, Sheehan JH, Kendall PL.
Expert Rev Clin Immunol. 2016 Jul;12(7):763-73. doi: 10.1586/1744666X.2016.1152888. Epub 2016 Mar 4. Review.
Gallant JN, Sheehan JH, Shaver TM, Bailey M, Lipson D, Chandramohan R, Red Brewer M, York SJ, Kris MG, Pietenpol JA, Ladanyi M, Miller VA, Ali SM, Meiler J, Lovly CM.
Cancer Discov. 2015 Nov;5(11):1155-63. doi: 10.1158/2159-8290.CD-15-0654. Epub 2015 Aug 18.
Computational and functional analyses of a small-molecule binding site in ROMK.
Swale DR, Sheehan JH, Banerjee S, Husni AS, Nguyen TT, Meiler J, Denton JS.
Biophys J. 2015 Mar 10;108(5):1094-103. doi: 10.1016/j.bpj.2015.01.022.
Donahue JP, Levinson RT, Sheehan JH, Sutton L, Taylor HE, Meiler J, D’Aquila RT, Song C.
J Virol. 2015 Feb;89(4):2415-24. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01981-14. Epub 2014 Dec 10.
NFI transcription factors interact with FOXA1 to regulate prostate-specific gene expression.
Grabowska MM, Elliott AD, DeGraff DJ, Anderson PD, Anumanthan G, Yamashita H, Sun Q, Friedman DB, Hachey DL, Yu X, Sheehan JH, Ahn JM, Raj GV, Piston DW, Gronostajski RM, Matusik RJ.
Mol Endocrinol. 2014 Jun;28(6):949-64. doi: 10.1210/me.2013-1213. Epub 2014 May 6.
Tailoring peptidomimetics for targeting protein-protein interactions.
Akram ON, DeGraff DJ, Sheehan JH, Tilley WD, Matusik RJ, Ahn JM, Raj GV.
Mol Cancer Res. 2014 Jul;12(7):967-78. doi: 10.1158/1541-7786.MCR-13-0611. Epub 2014 Mar 18. Review.
Small-molecule ligand docking into comparative models with Rosetta.
Combs SA, Deluca SL, Deluca SH, Lemmon GH, Nannemann DP, Nguyen ED, Willis JR, Sheehan JH, Meiler J.
Nat Protoc. 2013;8(7):1277-98. doi: 10.1038/nprot.2013.074. Epub 2013 Jun 6.
Egli M, Pattanayek R, Sheehan JH, Xu Y, Mori T, Smith JA, Johnson CH.
Biochemistry. 2013 Feb 19;52(7):1208-20. doi: 10.1021/bi301691a. Epub 2013 Feb 7.
Yang R, Shi J, Byeon IJ, Ahn J, Sheehan JH, Meiler J, Gronenborn AM, Aiken C.
Retrovirology. 2012 Apr 19;9:30. doi: 10.1186/1742-4690-9-30.
Measurement of aptamer-protein interactions with back-scattering interferometry.
Olmsted IR, Xiao Y, Cho M, Csordas AT, Sheehan JH, Meiler J, Soh HT, Bornhop DJ.
Anal Chem. 2011 Dec 1;83(23):8867-70. doi: 10.1021/ac202823m. Epub 2011 Nov 8.
Glycosylation of {beta}2 subunits regulates GABAA receptor biogenesis and channel gating.
Lo WY, Lagrange AH, Hernandez CC, Harrison R, Dell A, Haslam SM, Sheehan JH, Macdonald RL.
J Biol Chem. 2010 Oct 8;285(41):31348-61. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M110.151449. Epub 2010 Jul 16.
Dave S, Sheehan JH, Meiler J, Strange K.
Channels (Austin). 2010 Jul-Aug;4(4):289-301. Epub 2010 Jul 21.
Practically useful: what the Rosetta protein modeling suite can do for you.
Kaufmann KW, Lemmon GH, Deluca SL, Sheehan JH, Meiler J.
Biochemistry. 2010 Apr 13;49(14):2987-98. doi: 10.1021/bi902153g. Review.
Sheehan JH, Bunick CG, Hu H, Fagan PA, Meyn SM, Chazin WJ.
J Biol Chem. 2006 Feb 3;281(5):2876-81. Epub 2005 Nov 29.
Hu H, Sheehan JH, Chazin WJ.
J Biol Chem. 2004 Dec 3;279(49):50895-903. Epub 2004 Sep 27.
Designing sequence to control protein function in an EF-hand protein.
Bunick CG, Nelson MR, Mangahas S, Hunter MJ, Sheehan JH, Mizoue LS, Bunick GJ, Chazin WJ.
J Am Chem Soc. 2004 May 19;126(19):5990-8.