Patients with diabetes have a high risk of developing skeletal diseases accompanied by diabetic peripheral neuropathy (DPN). In this study, we isolated the role of DPN in skeletal disease with global and conditional knockout models of sterile-α and TIR-motif-containing protein-1 (Sarm1). SARM1, an NADase highly expressed in the nervous system, regulates axon degeneration upon a […]
Category: Publications
Development and Expansion of Intramuscular Adipose Tissue is Not Dependent on UCP-1-Lineage Cells in Mice (Links to an external site)
Accumulation of adipose tissue within and outside of skeletal muscle is associated with orthopedic injury and metabolic disease, where it is thought to impede muscle function. The close juxtaposition between this adipose and myofibers has led to hypotheses that paracrine interactions between the two regulate local physiology. Recent work suggests that intramuscular adipose tissue (IMAT) […]
Knockout of TSC2 in Nav1.8+ neurons predisposes to the onset of normal weight obesity (Links to an external site)
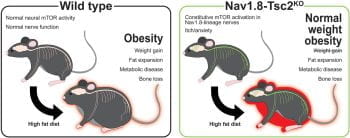
Obesity and nutrient oversupply increase mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) signaling in multiple cell types and organs, contributing to the onset of insulin resistance and complications of metabolic disease. However, it remains unclear when and where mTOR activation mediates these effects, limiting options for therapeutic intervention. The objective of this study was to isolate the role of constitutive […]
A bone-specific adipogenesis pathway in health and disease (Links to an external site)

Bone marrow adipocytes accumulate with age and in diverse disease states. However, their origins and adaptations in these conditions remain unclear, impairing our understanding of their context-specific endocrine functions and relationship with surrounding tissues. In this study, by analyzing bone and adipose tissues in the lipodystrophic ‘fat-free’ mouse, we define a novel, secondary adipogenesis pathway […]
Neuroskeletal Effects of Chronic Bioelectric Nerve Stimulation in Health and Diabetes (Links to an external site)

Background/Aims: Bioelectric nerve stimulation (eStim) is an emerging clinical paradigm that can promote nerve regeneration after trauma, including within the context of diabetes. However, its ability to prevent the onset of diabetic peripheral neuropathy (DPN) has not yet been evaluated. Beyond the nerve itself, DPN has emerged as a potential contributor to sarcopenia and bone disease; […]
Neural regulation of bone marrow adipose tissue (Links to an external site)
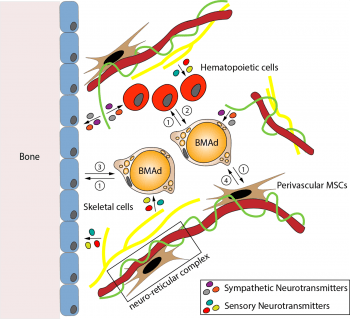
Bone marrow adipose tissue (BMAT) is an important cellular component of the skeleton. Understanding how it is regulated by the nervous system is crucial to the study of bone and bone marrow related diseases. BMAT is innervated by sympathetic and sensory axons in bone and fluctuations in local nerve density and function may contribute to […]
A neuroskeletal atlas: spatial mapping and contextualization of axon subtypes innervating the long bones of C3H and B6 mice (Links to an external site)
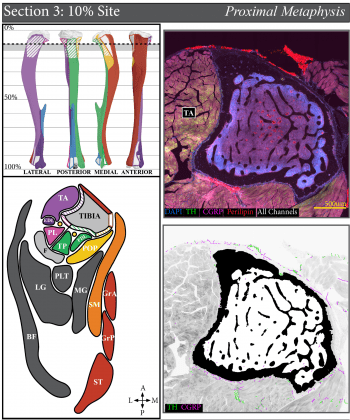
Nerves in bone play well‐established roles in pain and vasoregulation and have been associated with progression of skeletal disorders including osteoporosis, fracture, arthritis and tumor metastasis. However, isolation of the region‐specific mechanisms underlying these relationships is limited by our lack of quantitative methods for neuroskeletal analysis and precise maps of skeletal innervation. To overcome these […]
Microneedles for ultrasensitive biomarker detection (Links to an external site)

The detection and quantification of protein biomarkers in interstitial fluid is hampered by challenges in its sampling and analysis. Here we report the use of a microneedle patch for fast in vivo sampling and on-needle quantification of target protein biomarkers in interstitial fluid. We used plasmonic fluor—an ultrabright fluorescent label—to improve the limit of detection […]
Immunostaining of Skeletal Tissues (Links to an external site)

Immunostaining is the process of identifying proteins in tissue sections by incubating the sample with antibodies specific to the protein of interest, then visualizing the bound antibody using a chromogen (immunohistochemistry or IHC) or fluorescence (immunofluorescence or IF). Unlike in situ hybridization, which identifies gene transcripts in cells, immunostaining identifies the products themselves and provides […]
Marrow adipose tissue has distinct roles in glucose homeostasis (Links to an external site)
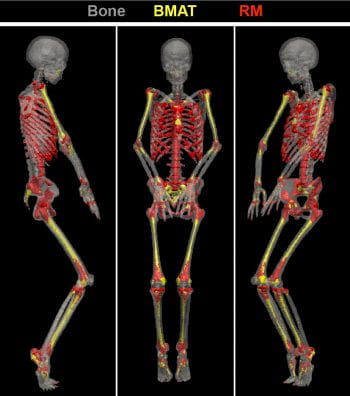
Great to see this manuscript come together in the Cawthorn lab after many years of hard work, including his brand new BMAT imaging and analysis techniques and lots of lingering data generated by Drs. Cawthorn and Scheller when they worked together as postdocs in the MacDougald lab (Dr. Scheller made some of the blots in […]
Refreshable Nanobiosensor Based on Organosilica Encapsulation (Links to an external site)

Implantable and wearable biosensors that enable monitoring of biophysical and biochemical parameters over long durations are highly attractive for early and presymptomatic diagnosis of pathological conditions and timely clinical intervention. Poor stability of antibodies used as biorecognition elements and the lack of effective methods to refresh the biosensors upon demand without severely compromising the functionality […]
Bone marrow adipose tissue does not express UCP1 (Links to an external site)
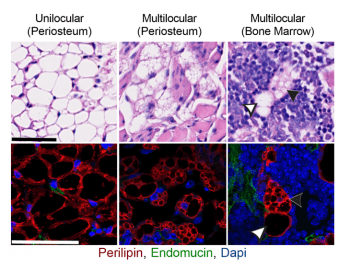
Adipocytes within the skeleton are collectively termed bone marrow adipose tissue (BMAT). BMAT contributes to peripheral and local metabolism, however, its capacity for cell-autonomous expression of uncoupling protein 1 (UCP1), a biomarker of beige and brown adipogenesis, remains unclear. To overcome this, Ucp1-Cre was used to drive diphtheria toxin expression in cells expressing UCP1 (Ucp1Cre+/DTA+). Despite […]
Shared Autonomic Pathways Connect Bone and Adipose Tissue. (Links to an external site)

Bone marrow adipose tissue (BMAT) is increased in both obesity and anorexia. This is unique relative to white adipose tissue (WAT), which is generally more attuned to metabolic demand. It suggests that there may be regulatory pathways that are common to both BMAT and WAT and also those that are specific to BMAT alone. The […]
Peripheral Neuropathy as a Component of Diabetic Skeletal Disease (Links to an external site)
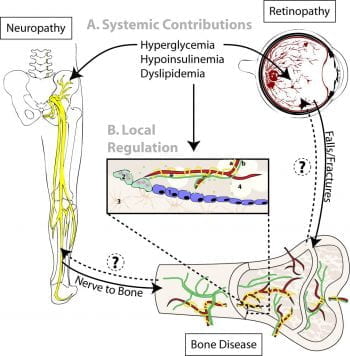
The goal of this review is to explore clinical associations between peripheral neuropathy and diabetic bone disease and to discuss how nerve dysfunction may contribute to dysregulation of bone metabolism, reduced bone quality, and fracture risk. In addition, we address therapeutic and experimental considerations to guide patient care and future research evaluating the emerging relationship […]
Nerves in bone: evolving concepts in pain and anabolism. (Links to an external site)

This review provides a historical perspective of the field of skeletal neurobiology which highlights the diverse yet interconnected nature of nerves and skeletal health, particularly in the context of bone anabolism and pain.
Exploiting Self-Capacitances for Wireless Power Transfer. (Links to an external site)
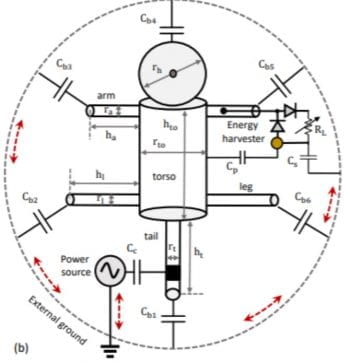
Conventional approaches for wireless power transfer rely on the mutual coupling (near-field or far-field) between the transmitter and receiver transducers. In this paper, we show that when the operational power-budget requirements are in the order of microwatts, a self-capacitance (SC)-based power delivery has significant advantages in terms of the power transfer-efficiency, receiver form-factor, and system […]
Characterization of the bone marrow adipocyte niche with 3D-EM. (Links to an external site)
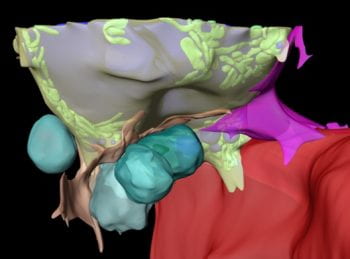
The bone marrow adipocyte (BMA) exists in a microenvironment containing unique populations of hematopoietic and skeletal cells. To study this microenvironment at the sub-cellular level, we performed a three-dimensional analysis of the ultrastructure of the BMA niche with focused ion beam scanning electron microscopy (FIB-SEM).
Bone marrow adipocytes resist lipolysis and β-adrenergic stimuli (Links to an external site)

Bone marrow adipose tissue (BMAT) is preserved or increased in states of caloric restriction. Similarly, we found that BMAT in the tail vertebrae, but not the red marrow in the tibia, resists loss of neutral lipid with acute, 48-hour fasting in rats. The mechanisms underlying this phenomenon and its seemingly distinct regulation from peripheral white […]
Evolution of the Marrow Adipose Tissue Microenvironment (Links to an external site)

In this review, we discuss the initial evolution of MAT in vertebrate lineages while emphasizing comparisons to the development of peripheral adipose, hematopoietic, and skeletal tissues. We then apply these evolutionary clues to define putative functions of MAT. Lastly, we explore the regulation of MAT by two major components of its microenvironment, the extracellular matrix […]