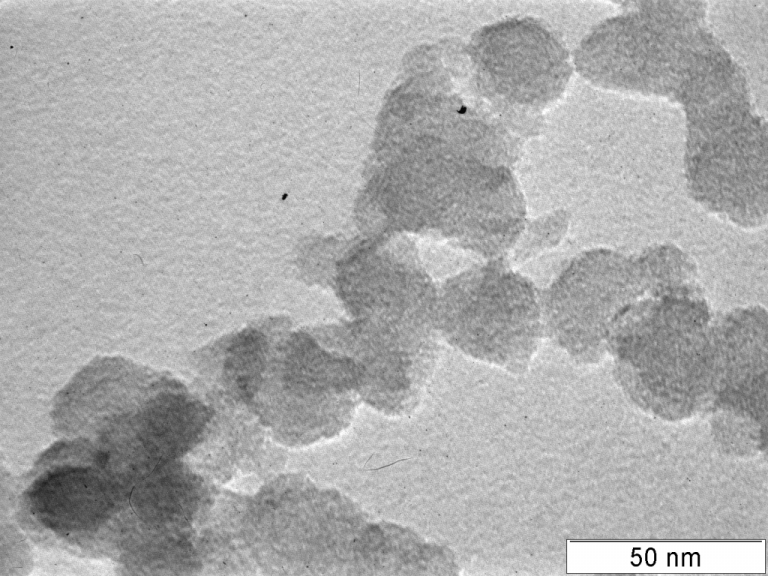
Health Effects of Combustion Particles
A better understanding of the mechanistic linkages between particle characteristics and observed health effects will lead to improved treatment and emission control strategies
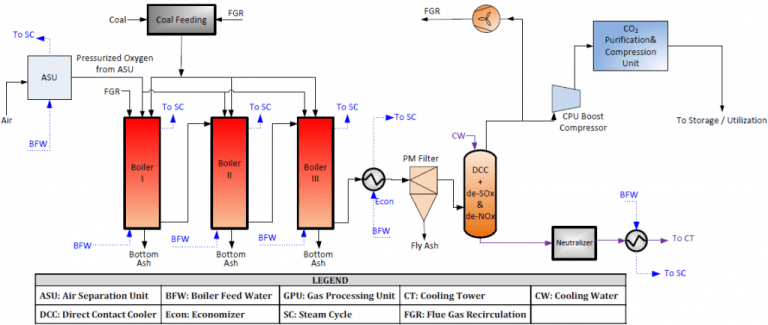
Pressurized Oxy-Combustion
The costs and energy penalty associated with the capture of carbon dioxide from power plants can be substantially reduced by employing advanced oxy-combustion methods. A team at WashU is developing the Staged, Pressurized Oxy-Combustion (SPOC) technology, which offers the potential for >90% carbon power production at a cost that is competitive with other low-carbon power sources.
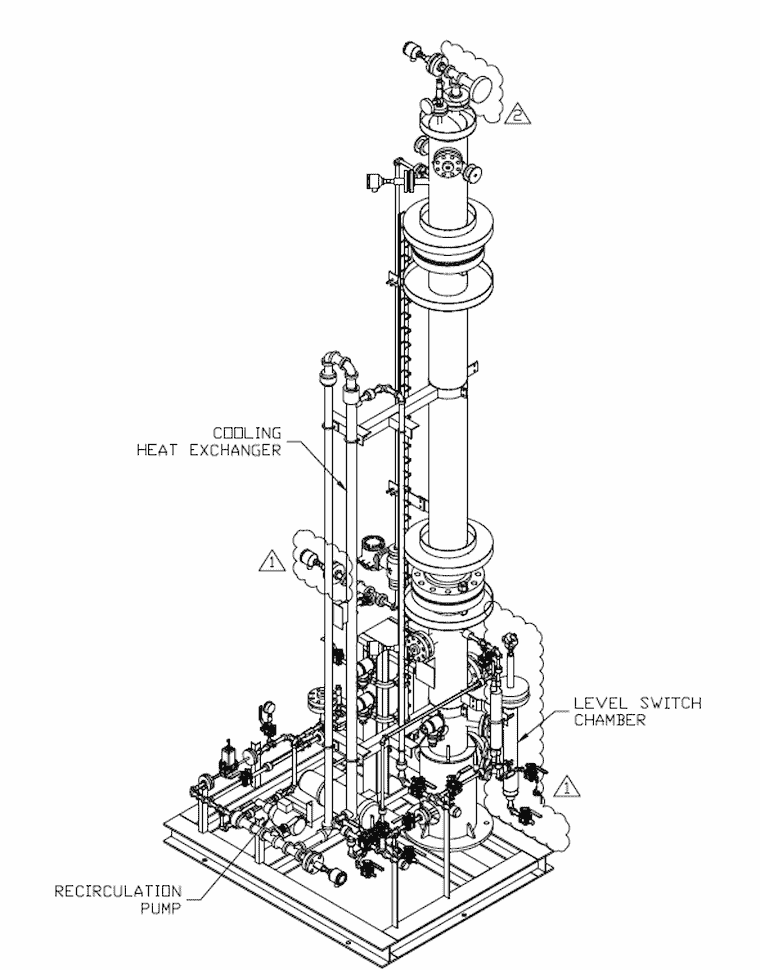
Integrated Pollutant Removal
In preparation for enhanced oil recovery or underground storage, captured carbon dioxide must be sufficiently purified. New approaches are investigated to co-capture contaminants such as SO2 and NOx, while recovering waste heat.
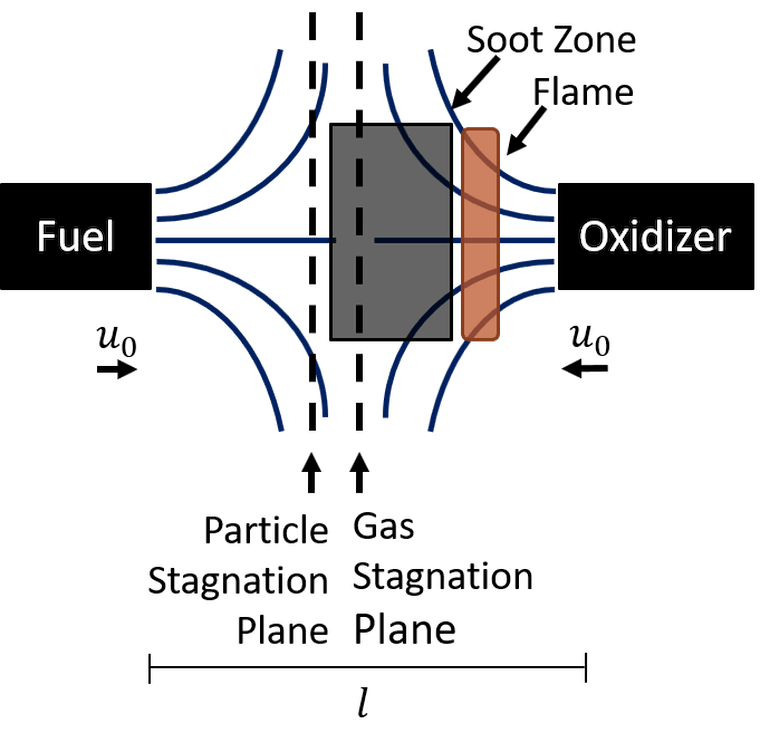
Soot Formation Modeling
The formation of ultra-fine particles in industrial boilers and furnaces influences radiation heat transfer. Emission to the atmosphere has adverse effects on environment and human health. Our research aims to understand how to effectively control particle formation and develop predictive models.

Biomass Co-Firing
Biomass may be co-fired with coal in existing boilers to reduce environmental impact. We examine how various pre-treatment processes affect combustion performance and emissions.