Screening Levels
The Screening Levels are chemical-specific concentrations for individual contaminants in air, drinking water and soil that may warrant further investigation or site cleanup.
| Resident Soil | Industrial Soil | Resident Air | Industrial Air | Tapwater |
| 1.6 mg/kg | 230 mg/kg | 0.042 μg/m3 | 0.18 μg/m3 | 4.0 μg/L |
Maximum Contaminant Level
The Maximum Contaminant Level (MCL) is the highest level of a contaminant that is allowed in drinking water.
MCL: 30 μg/L
National Primary Drinking Water Regulations for “Uranium” (Last Updated by the EPA in May 2009)
Uranium-235
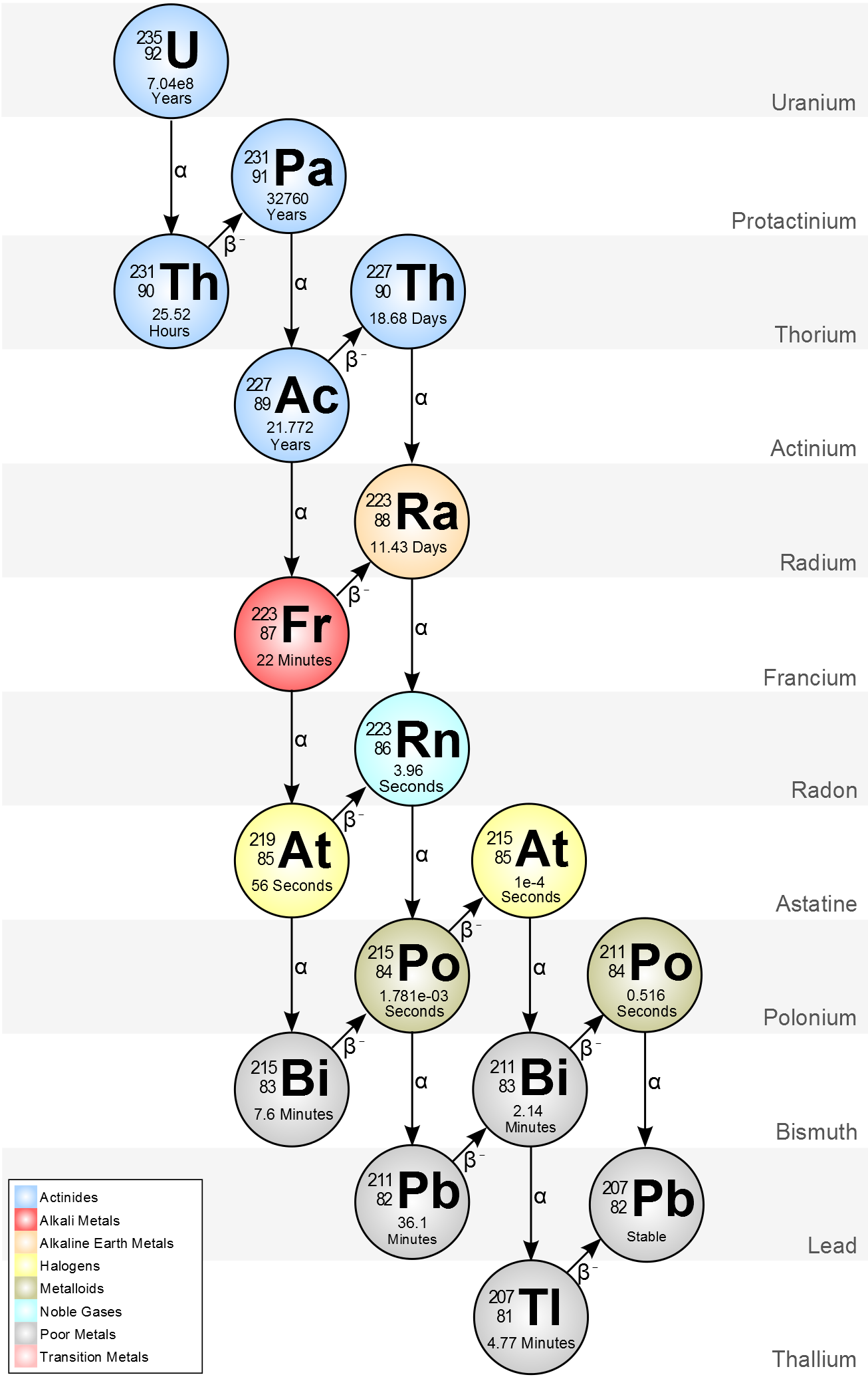
The stable isotope within the Uranium-235 decay chain is lead (Pb-207). In an area with Uranium-235 contamination, there could also be lead contamination.
Uranium-238
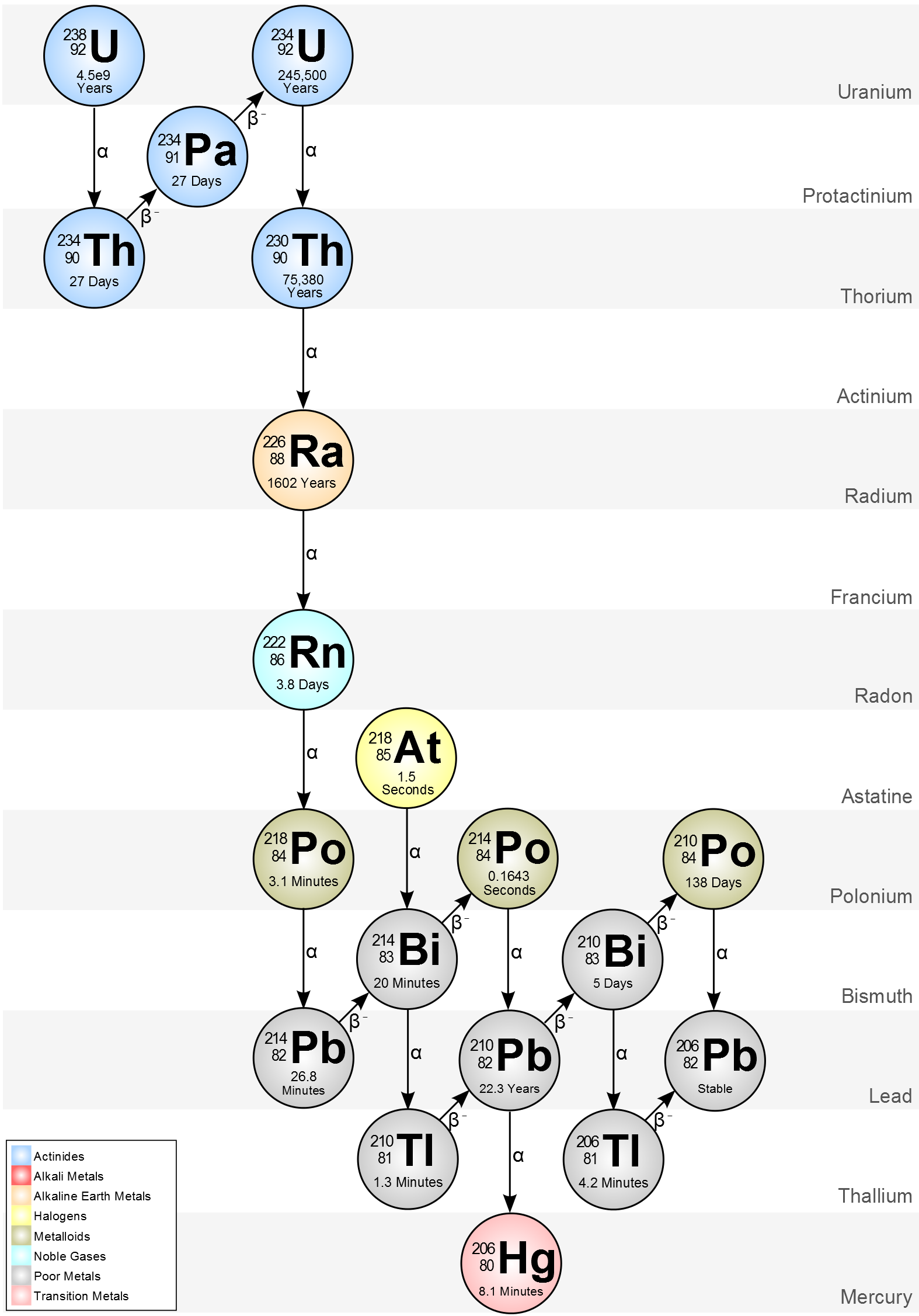
The stable isotope within the Uranium-238 decay chain is lead (Pb-206). In an area with Uranium-238 contamination, there could also be lead contamination.
Units
| Abbreviation | Meaning | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| mg/kg | mass of chemical (milligrams, mg) per mass of soil (kilogram, kg) | Equivalent to parts per million (ppm) |
| μg/m3 | mass of chemical (micrograms, mg) per volume of air (cubic meter, m3) | This can be converted to ppm using the molecular weight of the chemical |
| μg/L | mass of chemical (micrograms, μg) per volume of water (liter, L) | Equivalent to parts per billion (ppb); divide by 1,000 to get ppm |
For more information about these units and their conversion factors, visit https://cfpub.epa.gov/ncer_abstracts/index.cfm/fuseaction/display.files/fileid/14285.