Research Summary
The Harari lab is a multidisciplinary research group that brings together computational biologists, systems biologists, and bioinformaticians to study Alzheimer disease and related dementias. We use both traditional statistical and advanced machine learning approaches to analyze molecular data and provide novel insights on neurodegeneration.
Lab members work to discern how genes and other genetic factors contribute to the biological processes that effect Alzheimer disease via a multi-omic integrative approach. We develop and use innovative analytical workflows to study the genetic, transcriptomic, proteomic, metabolomic, and epigenetic data generated by single-nuclei and other tissue samples.
Areas of Research Focus
High-throughput and Cross-omics
High-throughput omics is the use of extraction, enrichment, and quantification of targeted biological material, and includes genomics, epigenomics, transcriptomics, proteomics, and metabolomics data.
Cross-omics approaches aim to integrate heterogenous biomolecular profiles and the use of high dimensional analytics to study not only how these profiles change with the disease, but also uncover the relationships and correlations between different biological molecules.
Machine Learning
Machine-learning based analyses use computational algorithms to apply statistical and model based approaches to data analysis. Several of theses methods include: supervised or unsupervised-based learning, regression based methods, Bayesian based methods, and deep learning methods.
We are using machine learning for high dimensional analysis of cross-omics data, and for a multitude of other analytics.
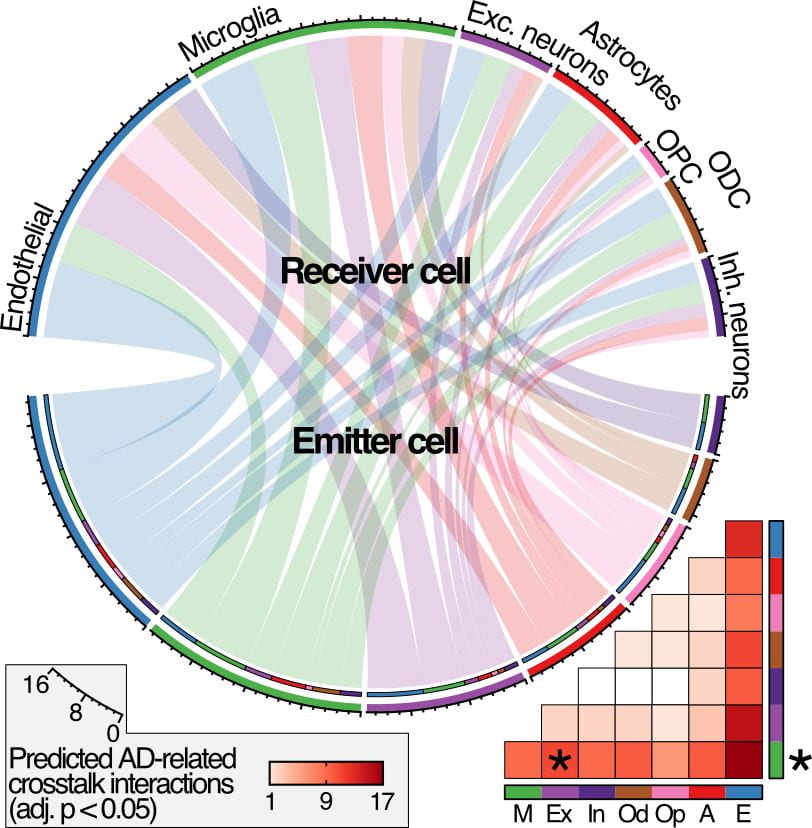
Single-cell genomics
Single-nucleus sequencing has emerged as a powerful approach to interrogate the underlying genomic or transcriptomic landscape of the cellularly-complex human brain.
We are currently using single nuclei RNA-seq (snRNA-seq), and single nuclei epigenetics (snATACseq), both with GWAS support to determine the cell type specific differences and unique transcriptional states in Alzheimer’s disease (AD) and Autosomal-Dominant AD (ADAD).
Data Science
The lab uses traditional statistical and machine learning techniques to discern results and meaning from the omics data collected. Data is also managed according to the FAIR guiding principles for data stewardship for findability, accessibility, interoperability, and reusability.
We are committed to making scientific data and processes open and reproducible. To support that commitment we have our data browsers and code available on the Resources page.




